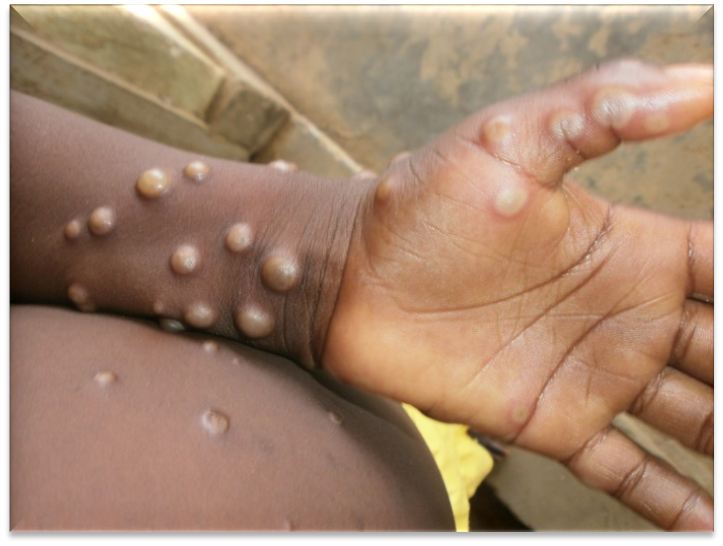
Mpox (previously known as monkeypox) is a viral disease caused by an orthopoxvirus called monkeypox virus. It spreads mainly through close contact with someone who has mpox, causing a painful rash, enlarged lymph nodes and fever. It can make people very sick and leave scars.
The disease mainly spreads from person to person through close contact. This includes, but isn’t limited to, sexual contact. Transmission occurs through exposure to bodily fluids; lesions on the skin or on internal mucosal surfaces, such as in the mouth or throat; respiratory particles; and contaminated objects.
In areas where animals carry the virus, mpox is a zoonotic disease, meaning it can spread from animals to humans. It’s found in tropical rainforests in central, east and west Africa, where small mammals such as squirrels, Gambian pouched rats, dormice, and various species of monkeys may be carriers.
Since May 2022, mpox has spread globally, with cases reported from countries without previously documented mpox transmission. The spread in most countries today is from people and not animals.