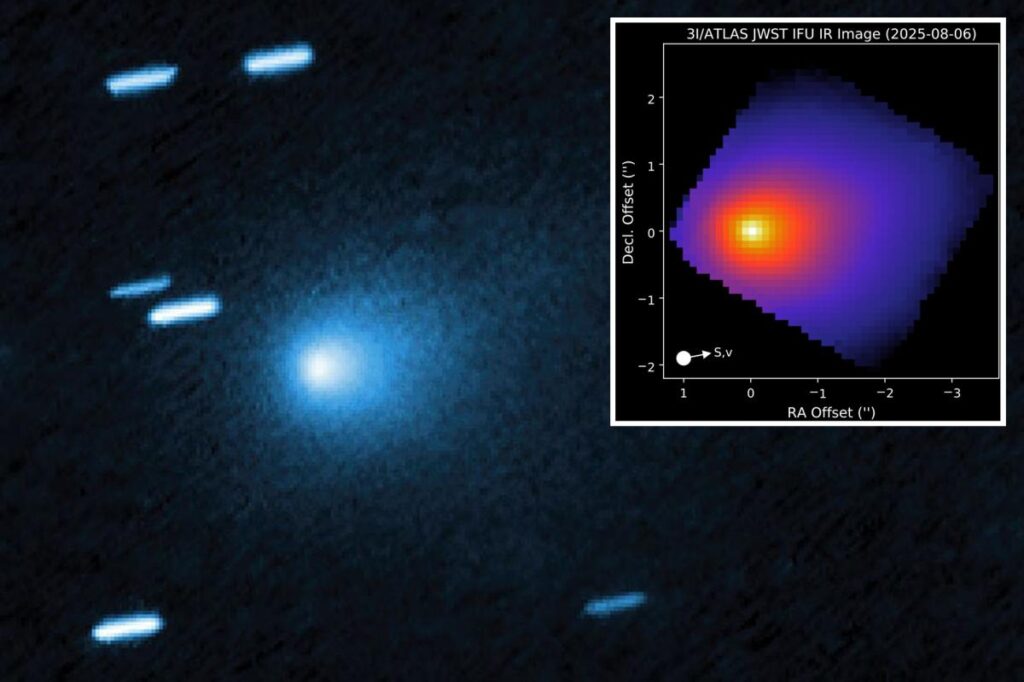
New images reveal the Manhattan-sized interstellar object 3I/ATLAS has started to sport a tail, indicating that it could possibly be a “maneuvering” alien craft, one Harvard scientist suggested.
After exhibiting signs of an incredibly strange “anti-tail” since first cropping up in the solar system in July, 3I/ATLAS is now showing evidence of a true cometary tail, images taken by Spain’s Nordic Optical Telescope in the Canary Island in September revealed.
These new images shows materials being peeled off behind the 33-billion ton object as it travels toward the sun and is hit with up to 33 gigawatts of solar radiation, Harvard astrophysicist Avi Loeb wrote in a recent paper.
However, the succession of an anti-tail and then the presence of a tail could be indicative of “controlled maneuvering” and a high-impact Black Swan event.
3I/ATLAS’s anti-tail was a plume composed of mostly carbon dioxide and water with trace amounts of cyanide and a never-seen-in-nature nickel alloy that has only been used in human manufacturing.
“[I]f the object is an alien spacecraft slowing down,” Loeb wrote, then the anti-tail would be evidence of a “braking thrust” maneuver which would naturally change to a tail as the slowing procedure completed.
The International Asteroid Warning Network added 3I/ATLAS to its list of targets earlier this week, and began monitoring the object for scientific purposes.
The group wrote on its website: “While it poses no threat, comet 3I/ATLAS present a great opportunity for the IAWN community to perform an observing exercise due to its prolonged observability from Earth and its high interest to the scientific community.”
Researchers around the globe are waiting with bated breath for the images taken earlier this month by NASA’s HiRISE camera — the highest resolution images of 3I/ATLAS yet — onboard the Mars orbiter when the object came within 12 million miles of the Red Planet.
They have yet to be shared by the US space agency due to the ongoing government shutdown.
3I/ATLAS will come closest to the sun on Oct. 29 when it will be 1.8 times further than the Earth is to the Sun.