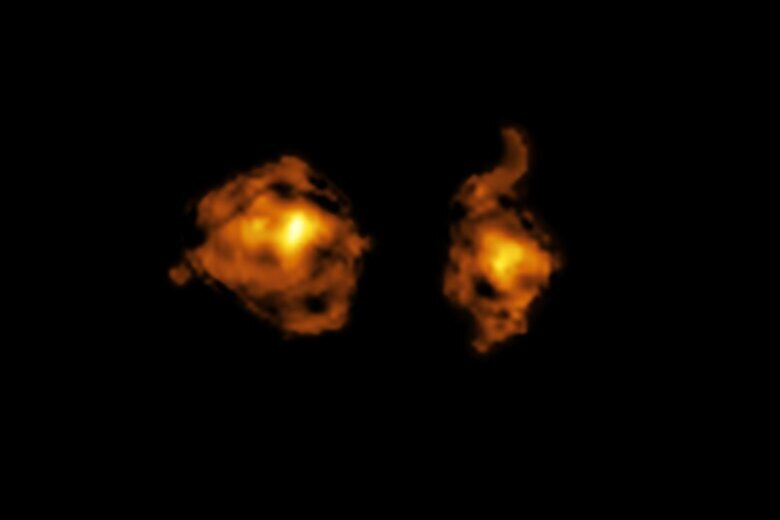
Astronomers have for the first time spotted two galaxies in the throes of a deep-space “duel.”

(CNN) — Astronomers have for the first time spotted two galaxies in the throes of a deep-space “duel.”
Using combined observations from ground-based telescopes over nearly four years, the researchers saw the distant galactic neighbors charging toward each other at more than 1.1 million miles per hour (1.8 million kilometers per hour). One repeatedly wielded its intense beams of radiation at the other, dispersing gas clouds and weakening its opponent’s ability to form new stars.
“That’s why we call it a ‘cosmic joust,’” said Pasquier Noterdaeme, a researcher for the Paris Institute of Astrophysics and the French-Chilean Laboratory for Astronomy in Chile who was part of the team that made the discovery.
What Noterdaeme and his colleagues spied was a distant snapshot of the two galaxies in the process of merging into one large galaxy 11 billion light-years away. The findings, described in a study published Wednesday in the journal Nature, provide a rare look into earlier times in the universe, when star formation and galaxy mergers were more common.
Zooming in
Working with the European Southern Observatory’s Very Large Telescope (VLT) and the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA) in Chile, the researchers found that the “attacking” galaxy’s piercing radiation comes from within its bright core, a quasar, powered by a supermassive black hole.
The intense gravitational influence of a black hole draws matter toward it in such an energetic way that dust and gas heat up to millions of degrees and become luminous, according to NASA. These luminous materials spiral around the black hole before entering, forming what’s called an “accretion disk,” and jets of energetic matter beam out away from the center.
Each blast of the quasar’s ultraviolet waves are about a thousand times stronger than the radiation of our Milky Way, causing hydrogen molecules from some of the “victim” galaxy’s star-forming nurseries to split and disperse, according to the study.
Stars form when large clumps of gas and dust reach a critical mass and collapse under their own gravity. However, researchers observed that after being dispersed by the radiation, the clouds were not dense or large enough to create new stars.
As additional material from the victim galaxy is drawn within reach of the supermassive black hole, it fuels the quasar with more energy. Quasars have been known to essentially “switch off” from time to time, said study coauthor Sergei Balashev, a researcher at the Ioffe Institute in St. Petersburg, Russia, which could give molecular clouds the opportunity to reform.
“It’s really the first time that we can see the radiative effect of a quasar on the molecular gas of a nearby galaxy,” Balashev said. Until now, this effect had only been theorized but not confirmed through direct observation.
Scientists initially wanted to observe this particular quasar more closely because of its unique features among thousands of low-resolution spectra, which are like fingerprints for distant celestial objects, offering clues about composition, temperature and activity within them.
“It’s really (like) finding a needle in a haystack,” Balashev said. However, the light from quasars is so powerful that it often outshines their own host galaxies, making it difficult to observe other galaxies close by, according to Noterdaeme, the study’s co-lead author.
Highly dynamic, luminous quasars are rare, according to NASA. Only about 1,000 of these objects are known to exist in the early days of the universe, Anniek Gloudemans, a postdoctoral research fellow at the National Science Foundation’s NOIRLab, previously told CNN via email.
“At first, we just knew there was some molecular gas between the (attacking galaxy’s) quasar and us. It’s only after, when we started to look with bigger telescopes, that we detected there were actually two galaxies,” Noterdaeme said.
While the dueling pair appears to be overlapping in the low-resolution spectra, the high-resolution imaging capabilities of ALMA revealed the galaxies are actually separated by thousands of light-years. Using the Very Large Telescope, the researchers were able to study the density and distance of the gas affected by the quasar’s radiation.
Since the light from these objects came from billions of light-years away in the early universe, it’s possible the two galaxies have already merged by now, but there is no way to be sure, Balashev said.
A blast from the past
Scientists believe quasars and galaxy mergers used to be far more common earlier in the universe’s lifetime, said Dong-Woo Kim, an astrophysicist with the Harvard and Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics who was not involved in the research.
Galaxies merge when they are pulled toward each other by gravity, and the universe used to be more densely packed together. Over time, the universe has expanded, and more galaxies have combined into larger ones, Kim said.
Noterdaeme said that 10 billion years ago was an interesting time in the universe, adding that astronomers call this period when stars formed at a rapid rate the “noon of the universe.”
Though less frequent, galaxy mergers are still happening all the time, Kim said. Even our own Milky Way is expected to merge with the Andromeda galaxy in a few billion years, but the study team isn’t certain yet whether the “cosmic joust” phenomenon is a common feature when two galaxies collide and form a larger one.
“It’s an exciting field to study,” Kim said. “Research like this can teach us more about the birth of new galaxies and observe how they evolve over time.”
The-CNN-Wire
™ & © 2025 Cable News Network, Inc., a Warner Bros. Discovery Company. All rights reserved.